The superstition warns that breaking a mirror leads to seven years of ill fortune, possibly as severe as causing death. People who follow this belief often take care when handling mirrors and sometimes engage in ‘corrective’ rituals when one is accidentally broken. Some common remedies include grinding the pieces into dust or burying the shards under moonlight to nullify the bad luck. In households, particularly in the past, such accidents could generate fear and anxiety, especially among domestic workers or those already affected by superstitious thinking. The number seven is thought to relate to the Roman belief that life renews itself every seven years, thus requiring a full renewal cycle before the curse lifts. Additionally, mirrors were long believed to reflect not just physical appearance but the soul itself—breaking one may symbolically ‘damage’ one’s spirit.
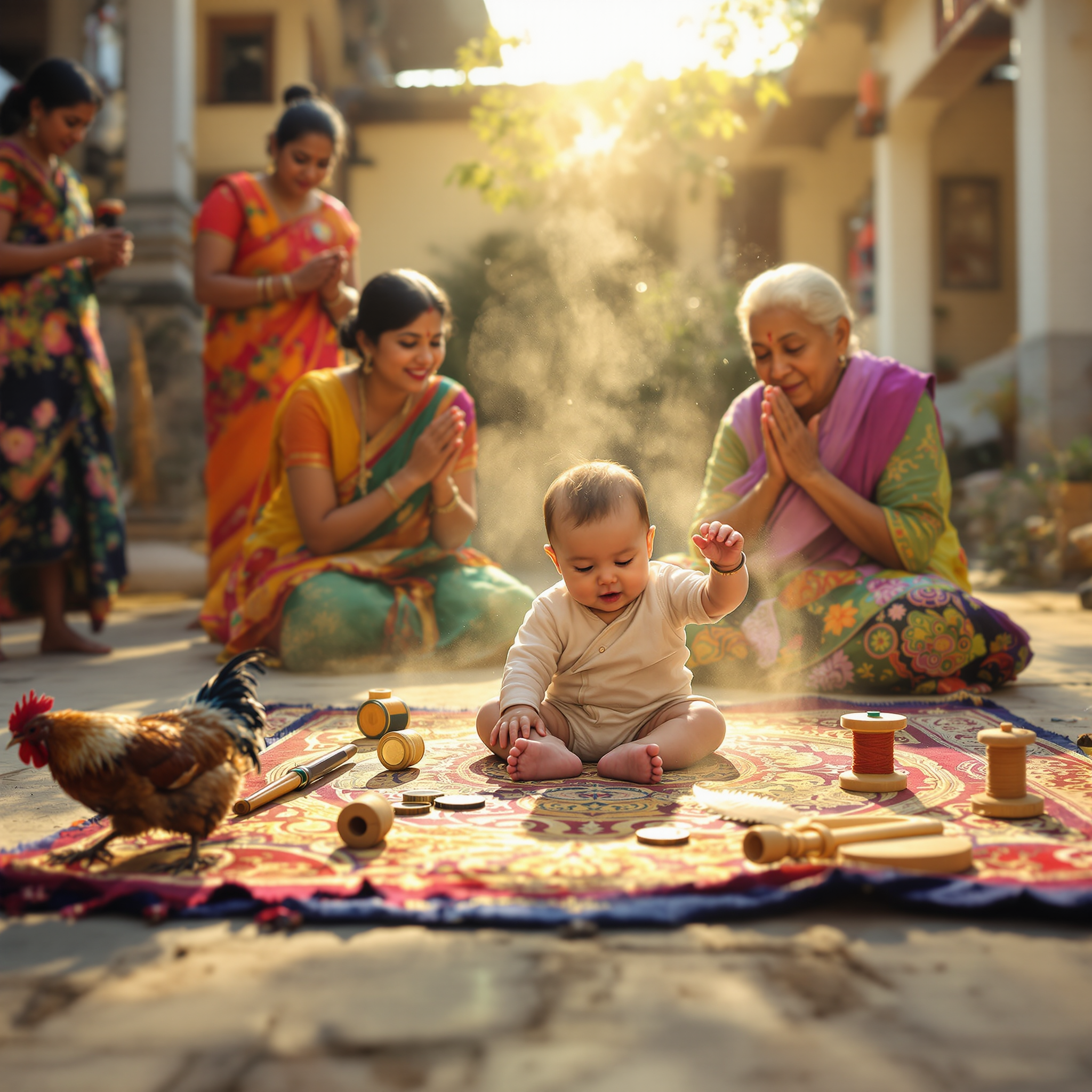

A baby’s future career or fate is predicted by the first object they select during a ceremonial setup.
In several Asian and Eastern European cultures, a traditional ceremony is held for babies usually around their first birthday. Known